< A version of this article was published in the July 2021 issue of Barks from the Guild, a publication of the Pet Professional Guild>
< A version of this article was published in the July 2021 issue of Barks from the Guild, a publication of the Pet Professional Guild>
< Updated 17NOV21 >
< A short link for this page – http://bit.ly/Canine-Stress >
A podcast about this article – https://bit.ly/WfMw-09OCT21-CanineStress >
Like us, our dogs can and do experience stress. Just as stress can make us feel afraid or hyper or edgy or irritable, it can do the same to our dogs. As a pet behavior consultant, I have observed that most behavior problems with pets, especially the more serious, such as aggression and separation anxiety, are related to one or more stressors in the animal’s life. It is a well-established fact that chronic stress can have a detrimental effect on our behavior, health, and overall well-being. If we want our dogs to have long and healthy lives, in my opinion, we also have an obligation to understand stress and its impact so we can do what is necessary to minimize stress in the lives of our canine friends.


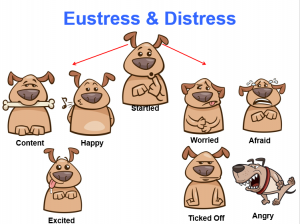
“Good” Stress versus “Bad” Stress
Certain levels of stress are normal and even necessary for survival and the development of gray matter in the brain. Often when people hear the word “stress,” they immediately start thinking about “distress” and the harm it can do.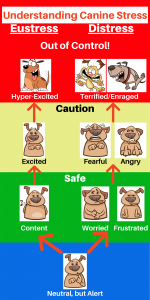 Distress is associated with negative emotions such as anger, fear, and sadness. Negative emotions are those that most of us avoid if given the opportunity. They are undesirable because they make us feel bad. The brain remembers these bad things in one trial, thereby learning to prevent suffering in the future. However, while limited amounts of distress can be good for us, the susceptibility to distress varies with each individual organism. How an individual responds to distress is often affected by a combination of inherited genes and events within the organism’s environment. Distress can start as an acute incident and rapidly become chronic until an organism collapses in exhaustion or self-destructs.
Distress is associated with negative emotions such as anger, fear, and sadness. Negative emotions are those that most of us avoid if given the opportunity. They are undesirable because they make us feel bad. The brain remembers these bad things in one trial, thereby learning to prevent suffering in the future. However, while limited amounts of distress can be good for us, the susceptibility to distress varies with each individual organism. How an individual responds to distress is often affected by a combination of inherited genes and events within the organism’s environment. Distress can start as an acute incident and rapidly become chronic until an organism collapses in exhaustion or self-destructs.
Yet, people do not always consider the positive aspects of stress. They may, therefore, not be familiar with the term eustress. Eustress allows an organism to utilize energy positively and assists in the development of new capabilities. A positive emotion associated with eustress is happiness. Positive emotions are those that most of us enjoy experiencing because they are pleasant. Eustress, in appropriate quantities, is essential to normal growth. However, as with most things in life, too much of anything can be detrimental.
Both eustress and distress occur over a continuum, as illustrated in the graphic “Understanding Canine Stress.”
Whether stress is “distress” or “eustress,” physiologically, the manifestation of stress in dogs is similar to that in humans, with the same negative and positive effects. Stress can make an individual ill, suppress the immune system, cause behaviors that damage relationships with others, and increase arousal. Furthermore, this increase in arousal dramatically increases the probability of inappropriate and even aggressive behavior.
Eustress can range from contentment to excitement to hyper-excitement. Distress can begin with worry, transform to fear, and end in terror. Likewise, frustration can lead to anger and then rage. As the intensity of the emotion increases, an organism reaches a tipping point where it goes into a classic “fight or flight” response.
Physiological Effects of Stress
When something stressful happens, we (or animals) are startled or frightened, experience physical pain, or are at a high state of emotional arousal due to distress or eustress; our body falls under the control of the sympathetic  autonomic nervous system (SANS), which is responsible for controlling the fight or flight response. This occurs when our bodies go on autopilot to protect us from the perceived threat.
autonomic nervous system (SANS), which is responsible for controlling the fight or flight response. This occurs when our bodies go on autopilot to protect us from the perceived threat.
The SANS is closely associated with the limbic system, the section of the brain that deals with the expression and experience of emotions, storage of memories, and expression of aggression. It is the most primitive part of the brain and is very involved with instinctual survival mechanisms. It is separate from the cerebral cortex, which is thought to be the “thinking” part of the brain and the site of conscious thought and intelligence. Remember, the brain is hard-wired to always remember negative emotional responses to help ensure our future safety.
When the limbic system (emotional autopilot) is activated, the cerebral cortex is suppressed. This is why one does not typically behave rationally when in a highly charged emotional state. It is also why expecting our dogs to respond to a well-trained cue when they are in distress is usually a futile effort. Likewise, the parts of the brain responsible for learning something new are shut down at this time. Conversely, when the cerebral cortex is highly active, the limbic system is suppressed.
suppressed.
During a stressful situation, the release of various neurotransmitters and stress hormones triggers a plethora of reactions within the body that shuts down all the systems not necessary for survival. For example, adrenaline levels, a neurotransmitter, become elevated, increasing pulse rate, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and dilation of bronchial tubes and pupils, preparing the body for the surge of energy necessary for the fight or flight response. Cortisol production also increases, suppressing the immune system and other systems not essential for our short-term survival. (See Recommended Resources for more information.)
After the stressful situation has passed, the body’s stress response is supposed to  “turn off,” and neurotransmitters and stress hormones should return to normal levels. However, these changes do not “turn off” instantly but can take 24 to 72 hours to return to their normal (non-stress) levels. As a result, if an organism is exposed to frequent stress events (daily or multiple times per day), those levels may never return to normal. This can place the individual in a chronic state of stress. For example, think of the dog that aggressively reacts to the mail carrier Monday through Saturday of every week. That dog’s stress levels may never get a chance to return to normal. The same can happen with the dog that demands to play fetch every day. While fetching the ball is a positive emotional event for most dogs, for some, it can cause such a state of euphoria that they can become obsessive about it. This positive emotional response turns into the negative emotion of frustration.
“turn off,” and neurotransmitters and stress hormones should return to normal levels. However, these changes do not “turn off” instantly but can take 24 to 72 hours to return to their normal (non-stress) levels. As a result, if an organism is exposed to frequent stress events (daily or multiple times per day), those levels may never return to normal. This can place the individual in a chronic state of stress. For example, think of the dog that aggressively reacts to the mail carrier Monday through Saturday of every week. That dog’s stress levels may never get a chance to return to normal. The same can happen with the dog that demands to play fetch every day. While fetching the ball is a positive emotional event for most dogs, for some, it can cause such a state of euphoria that they can become obsessive about it. This positive emotional response turns into the negative emotion of frustration.  Frustration may cause the dog to start demand barking and become aggressive when the person no longer plays the game. That can also lead to chronic stress and its debilitating effects on the body. Sometimes when an individual is subjected to chronic stress, the mechanisms that are supposed to turn off the production of stress hormones cease to function, so ‘within a few days, four times as much cortisol as normal is present, (Scholz & von Reinhardt, 2007) potentially creating a critical mental and physical health crisis.
Frustration may cause the dog to start demand barking and become aggressive when the person no longer plays the game. That can also lead to chronic stress and its debilitating effects on the body. Sometimes when an individual is subjected to chronic stress, the mechanisms that are supposed to turn off the production of stress hormones cease to function, so ‘within a few days, four times as much cortisol as normal is present, (Scholz & von Reinhardt, 2007) potentially creating a critical mental and physical health crisis.
What Does Stress Feel Like?
Stress affects us both physiologically and emotionally, and the two are always interconnected. Whether experiencing eustress or distress, the physiology and the effects on the body are essentially the same. Therefore, the most significant difference between the two types of stress is our perception of how we feel.
difference between the two types of stress is our perception of how we feel.
We have all experienced both eustress and distress at some point in our lives. Fortunately, not all of us have experienced extreme eustress or distress. Some medications can cause the same physiological effect as distress. One such medication is Prednisone.
Prednisone is a manufactured corticosteroid used to reduce inflammation. It is used to treat autoimmune disorders, asthma, lupus, colitis, Bell’s palsy, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory diseases. Prednisone mimics  cortisol, a stress hormone. Therefore, the side effects of prednisone can be similar to those of an organism experiencing extreme stress. These side effects include; insomnia, euphoria, depression, mania, mood swings, irritability, and even psychotic behavior. As an asthmatic, I have been prescribed a course of prednisone numerous times and know how it makes me feel. While it eventually makes me physically healthier, the side effects are not pleasant for me or those around me. I have also observed animals on prednisone, and sometimes they can react negatively and experience significant behavioral changes, which do not always resolve long after the drug is no longer being used. I often share this experience with my clients because they have a greater appreciation for how their dog feels under extreme stress if they have ever taken prednisone.
cortisol, a stress hormone. Therefore, the side effects of prednisone can be similar to those of an organism experiencing extreme stress. These side effects include; insomnia, euphoria, depression, mania, mood swings, irritability, and even psychotic behavior. As an asthmatic, I have been prescribed a course of prednisone numerous times and know how it makes me feel. While it eventually makes me physically healthier, the side effects are not pleasant for me or those around me. I have also observed animals on prednisone, and sometimes they can react negatively and experience significant behavioral changes, which do not always resolve long after the drug is no longer being used. I often share this experience with my clients because they have a greater appreciation for how their dog feels under extreme stress if they have ever taken prednisone.
Causes of Stress in Dogs
Brambell’s Five Freedoms
An animal typically experiences distress when its most basic needs are not met. One of the first and most comprehensive efforts to define an animal’s most basic welfare needs started in Great Britain in 1965 with the establishment of the Brambell Commission. This commission, created by Parliament, was charged with reviewing the treatment of farm animals and developing a minimum standard for meeting their needs. They wrote a document known as “The Five Freedoms,” which is an excellent starting point for evaluating the welfare of any animal, including companion dogs. The five freedoms are:
One of the first and most comprehensive efforts to define an animal’s most basic welfare needs started in Great Britain in 1965 with the establishment of the Brambell Commission. This commission, created by Parliament, was charged with reviewing the treatment of farm animals and developing a minimum standard for meeting their needs. They wrote a document known as “The Five Freedoms,” which is an excellent starting point for evaluating the welfare of any animal, including companion dogs. The five freedoms are:
- Ensure your dog is free from hunger, thirst, and malnutrition.
This sounds relatively simple — provide your dog with food and water, and you have complied with this first freedom. However, I encourage you to give this more thought. Is the food you feed your dog wholesome and a type that would be in their natural diet? Are they allowed to consume this food in a manner that is natural for their species? We also must consider that too much food is equally bad, as evidenced by the significant number of obese dogs we see today.
- Ensure your pet is free from discomfort.
Again, this freedom seems relatively straightforward — make sure your pet always has adequate shelter from temperature and weather extremes. However, there is much more to comfort than hot versus cold and dry versus damp.
Your dog also needs a quiet, comfortable resting place where they can be undisturbed and where they will feel safe. You need to make sure that their  environment is free from things that may cause them harm.
environment is free from things that may cause them harm.
Your dog’s breed also affects what they need to be comfortable. For example, if they have long hair, they may be unable to groom themselves adequately. If that is the case, their guardian must groom them regularly so that their hair does not become tangled and matted, causing them discomfort.
Obesity puts a strain on the joints and may cause pain and discomfort, so it is essential to monitor how much we feed our dogs so they do not become overweight.
Lastly, like humans, dogs are social animals. They may depend on interactions with others, particularly of their species, to be comfortable. However, if they do not feel safe around other dogs, being compelled to live with another dog may cause discomfort. Therefore, knowing and responding correctly to your dog’s social needs is critical, as is putting their needs above our own where necessary.
- Ensure your pet is free from pain, injury, and disease.
You can easily meet the requirements of this freedom by ensuring that your pet receives routine veterinary care. In addition, a weekly body check by you can alert you to any changes in your pet’s physical condition.
Being free from pain is very similar to being free from discomfort, so the dog’s grooming needs must again be considered. Remember, dogs are designed by nature not to show pain and thus weakness, so often they will attempt to hide their pain. Obesity and matted coats may both cause pain.
Since the use of aversives in training are specifically designed to cause an animal emotional or physical discomfort, we must ensure such methods and tools are never used with our dogs.
- Ensure your pet is free to express normal behaviors.
To meet this requirement, you first need to know and understand what constitutes normal and abnormal canine behavior. Unfortunately, this can be difficult because there is so much incorrect information about canine behavior circulating as myths and perpetuated in outdated books and inaccurate websites.
What we know about canine behavior today has changed dramatically since the 1970s. Many of the old “truths” are false. Statements such as “Dogs are like  wolves,” “Dogs are pack animals,” “You must be ‘dominant’ or ‘alpha’ over your dog,” and “Dogs need to be trained with choke collars, shock collars, and alpha wolf rollovers, and other types of intimidation” are both false and harmful. While some might maintain that such statements are supported by scientific research, this is not the case. Managing and training a dog with aversives is highly likely to cause unnecessary and extreme distress for both parties. Indeed, based on what we know about distress, if either the dog or the handler is in a negative emotional state, they are more likely to be irritable, irrational, potentially aggressive, and less likely to be able to learn. This is no way to build or maintain a relationship. (See Recommended Resources for more information.)
wolves,” “Dogs are pack animals,” “You must be ‘dominant’ or ‘alpha’ over your dog,” and “Dogs need to be trained with choke collars, shock collars, and alpha wolf rollovers, and other types of intimidation” are both false and harmful. While some might maintain that such statements are supported by scientific research, this is not the case. Managing and training a dog with aversives is highly likely to cause unnecessary and extreme distress for both parties. Indeed, based on what we know about distress, if either the dog or the handler is in a negative emotional state, they are more likely to be irritable, irrational, potentially aggressive, and less likely to be able to learn. This is no way to build or maintain a relationship. (See Recommended Resources for more information.)
The Pet Professional Guild (PPG) and the American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) have been instrumental in refuting the many myths about canine  behavior and training. If you wish to learn more, I encourage you to read the PPG’s many position statements at https://www.petprofessionalguild.com/Position-Statements, where you can also find citations to the peer-reviewed scientific literature supporting what we know about canine behavior.
behavior and training. If you wish to learn more, I encourage you to read the PPG’s many position statements at https://www.petprofessionalguild.com/Position-Statements, where you can also find citations to the peer-reviewed scientific literature supporting what we know about canine behavior.
Another excellent resource, especially for veterinarians, is the AAHA’s 2015 Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines. Every veterinarian should be thoroughly familiar with this document. You read the guidelines at https://www.aaha.org/aaha-guidelines/behavior-management/behavior-management-home/
In my 26 plus years of experience, the freedom to express normal behaviors is the freedom that pet parents most often overlook. Many are unaware of the vast repertoire of normal dog behaviors. Because they find some of these behaviors undesirable from a human perspective, such as “butt sniffing,” they categorize them as” abnormal.” It is imperative that a pet parent the times to learn what constitutes normal behavior for a dog. The best way for them to do so is to enroll in a dog training class taught by an individual who has been certified by either the Pet Professional Accreditation Board (PPAB) or the Certification Council for Professional Dog Trainers (CCPDT). Minimally, they want to make sure their trainer is a member of the Pet Professional Guild (PPG). (See Recommended Resources for more information.)
Your dog needs adequate space to explore and an enriched environment to stimulate their minds and bodies to express normal behaviors. The ability to sniff and explore the world is key to a dog’s life. Dog walks are more important for opportunities to sniff than they are for physical exercise. If you are a power-walker who likes to walk the same route as fast as you can, your dog will probably be happier at home.
opportunities to sniff than they are for physical exercise. If you are a power-walker who likes to walk the same route as fast as you can, your dog will probably be happier at home.
Toys enrich your pet’s environment by giving them something to play with; however, your dog also needs appropriate interaction with living things as well. That can come from other dogs and us, and perhaps even other companion animals, depending on the dog.
Playing with your dog is good for establishing and maintaining a lifelong bond. It is also an excellent outlet for mental and physical activity and can be just plain fun! However, it is essential to understand that play,  especially very active play, is stressful in itself and increases your dog’s arousal level. Therefore, play should be frequently interrupted, and as soon as the dog has calmly settled, they can be rewarded with more play. If the dog does not or cannot settle, then play stops.
especially very active play, is stressful in itself and increases your dog’s arousal level. Therefore, play should be frequently interrupted, and as soon as the dog has calmly settled, they can be rewarded with more play. If the dog does not or cannot settle, then play stops.
Overly rough play between a person and a dog, especially play where the dog exhibits mouthing, and nipping behavior is inappropriate. For the safety of others, as well as yourself, nipping must ALWAYS be discouraged. The best way to prevent such play is to stop playing when it occurs immediately. To do so effectively, guardians need to learn to recognize the signs that indicate their dog’s level of arousal is increasing so that they can stop play before any mouthing occurs.
While our dogs, hopefully, enjoy our companionship, many of them also need adequate opportunities to interrelate with others of their own kind in a positive situation. That does not mean you need to have more than one dog, but it does mean your dog may benefit from having some suitable doggie friends in the neighborhood or at doggie daycare. However, ideally, these friends must be of a similar temperament, age, size, and playstyle as much as possible. In addition, the interactions must be enjoyable for all parties.
Lastly, not all dogs enjoy the company of other dogs, just as many people do not particularly appreciate interacting with other people. In this case, it is essential to understand that you cannot make a dog like another dog or a person.
- Ensure your pet is free from fear and distress.
I genuinely believe that no psychologically healthy human would ever intentionally cause their dog fear or distress. However, lack of knowledge or incorrect perceptions and beliefs about canine behavior can undoubtedly cause a great deal of fear and distress in our canine companions. As a behavior consultant, I see many dogs for “aggression” that is almost always based on stress-related fear.
Puppy Socialization
Preventing future fear in a puppy starts during their critical period, when we first typically bring them into our lives at 8-weeks of age. Unfortunately, this is a short amount of time, as this period ends between 12 and 16 weeks of age.
During this time, most puppies accept new environments, people, and situations. However, it is essential to plan those interactions, so they are a positive experience. A socialization event that a puppy finds distressing can be a significant setback. This is where working with a properly credentialed professional trainer can be helpful. (See Recommended Resources for more information.)
Although a dog’s critical period ends by 16-weeks of age, you should never stop exposing your dog to new things while associating the experience with a high-value reward. This should continue throughout the pet’s life. Of course, a dog can be desensitized after 12 to 16 weeks of age, but I recommend that guardians work with a certified dog behavior consultant to help them develop a remedial socialization program that will be beneficial and not risk causing harm.
A lack of adequate physical and mental stimulation can also cause a dog to become anxious and fearful. A dog needs a moderate amount of both physical and mental exercise regularly. A dog that does not get adequate physical and mental enrichment may become bored and frustrated and start exhibiting behaviors guardians may find undesirable. On the other hand, too much stimulation and exercise can also be detrimental, causing a state of chronic stress. Throwing the ball 20 to 50 times daily and daily visits to the dog park or a doggie daycare are often counter-productive and unhealthy as they can also lead to chronic stress. Activities need to be well balanced with ample opportunities for rest. Remember, a dog typically sleeps 17 hours per day.
mental enrichment may become bored and frustrated and start exhibiting behaviors guardians may find undesirable. On the other hand, too much stimulation and exercise can also be detrimental, causing a state of chronic stress. Throwing the ball 20 to 50 times daily and daily visits to the dog park or a doggie daycare are often counter-productive and unhealthy as they can also lead to chronic stress. Activities need to be well balanced with ample opportunities for rest. Remember, a dog typically sleeps 17 hours per day.
When we add a dog to our family, we bring them into a very foreign environment and culture with very different rules. On top of that, we expect them to understand a foreign language while we often make no effort to learn their language. We need to educate our dogs to live in our world and educate ourselves about the dog world to keep them free from fear and distress.
We also need to actively protect our dogs by avoiding stressful situations until they have had adequate socialization and training. As guardians, we must take responsibility for managing their interactions with the environment and other living things.
Lastly, understand that dogs are exceptionally good at reading human emotional states, especially those that live with them. They do it by observing our body language and facial expression, our behavior, the tone of our voice, and even our scent. Unfortunately, they are not as good at knowing why we are emotionally upset. If we are angry with our spouse or kids, frightened because a car almost hit us, grieving at the loss of a family member, or ecstatic because we just won the lottery, our dogs do not know why. Because they do not understand why we are upset, they may change their behavior towards us.
Fear Responses
What does an animal do when they are afraid? Animals, humans included, have four typical responses when they are scared; Flee, Fight, Freeze, and Fidget About (see the image below).
 Flee: This is self-explanatory and is all about the fight or flight response. It is essential to understand that when a dog is on a leash, they know that they cannot run away from what is scaring them. The inability to flee is why a dog may be more reactive when they are on a leash. Instead, they desperately try to scare whatever they are afraid of, such as another dog, a person, a cyclist, etc. This is not, however, an excuse to have a reactive dog off-leash. A known reactive dog should ALWAYS be on a regular 6-ft leash or inside a securely fenced area when they are outside of your home. It is essential to keep them out of situations where they react like this. Every time such a reaction occurs, it becomes more likely to happen again. (See Recommended Resources for more information.)
Flee: This is self-explanatory and is all about the fight or flight response. It is essential to understand that when a dog is on a leash, they know that they cannot run away from what is scaring them. The inability to flee is why a dog may be more reactive when they are on a leash. Instead, they desperately try to scare whatever they are afraid of, such as another dog, a person, a cyclist, etc. This is not, however, an excuse to have a reactive dog off-leash. A known reactive dog should ALWAYS be on a regular 6-ft leash or inside a securely fenced area when they are outside of your home. It is essential to keep them out of situations where they react like this. Every time such a reaction occurs, it becomes more likely to happen again. (See Recommended Resources for more information.)
Fight: Becoming aggressive is also part of the fight or flight response. Allowing a dog to react in this manner can be a liability risk and a safety risk for the dog’s handler and others. Dogs can do an incredible amount of severe damage in a very short amount of time. It is a dog’s guardian’s responsibility to prevent this type of behavior. As explained with fleeing, a dog on a leash comprehends that the leash will restrain them from fighting effectively. It can also worsen if two dogs on leash are fighting and the leashes become entangled. Separating dogs in this scenario is complex and risky. Again, none of this is an excuse to have a reactive dog off-leash.
It is essential to keep dogs who may behave aggressively out of situations and environments where they could attack another person or animal because there is always a risk of severe injury or even death. Every time such a reaction occurs, it becomes more likely to happen again. Dogs that have attacked other dogs should never be taken to a dog park or a doggie daycare.
Freeze: This involves becoming totally rigid and immobile. It is essentially the absence of any behavior that the dog feels could be provocative. Freezing often occurs when the dog’s emotional state has moved from being afraid to being  terrified. Dog guardians often misunderstand freezing. Since their dog is non-reactive (not vocalizing or moving), guardians assume the dog is “fine,” when in reality, they are terrified. A terrifying incident of this nature is unlikely to be forgotten. When a dog freezes in fear, it is incumbent upon its guardian to carefully and quietly remove them from that situation as quickly as possible.
terrified. Dog guardians often misunderstand freezing. Since their dog is non-reactive (not vocalizing or moving), guardians assume the dog is “fine,” when in reality, they are terrified. A terrifying incident of this nature is unlikely to be forgotten. When a dog freezes in fear, it is incumbent upon its guardian to carefully and quietly remove them from that situation as quickly as possible.
Fidget About: This is essentially the dog exhibiting a normal behavior in an abnormal context, aka a displacement behavior. This may be as simple as looking away, sniffing, or playing with a toy. It is the dog’s way of ignoring what they perceive as threatening with the hope that the threat will ignore them and go away.
The critical thing to remember with any of the four F’s (Flee, Fight, Fidget About, or Freeze) is that we want to minimize putting our dogs in these situations once we know any of these behaviors is a likely possibility. The brain is designed to remember scary things after the very first event. Subsequent exposures will just reduce the probability of ever being able to move beyond this fear.
Identifying Stress in Canines
Dogs express themselves and communicate with vocalizations, body language, and behavior. By getting familiar with our dogs’ bodies, we can tell when they start to feel stressed. It is imperative to look at the entire body and not just isolated parts to get the best understanding of what our dogs are feeling.
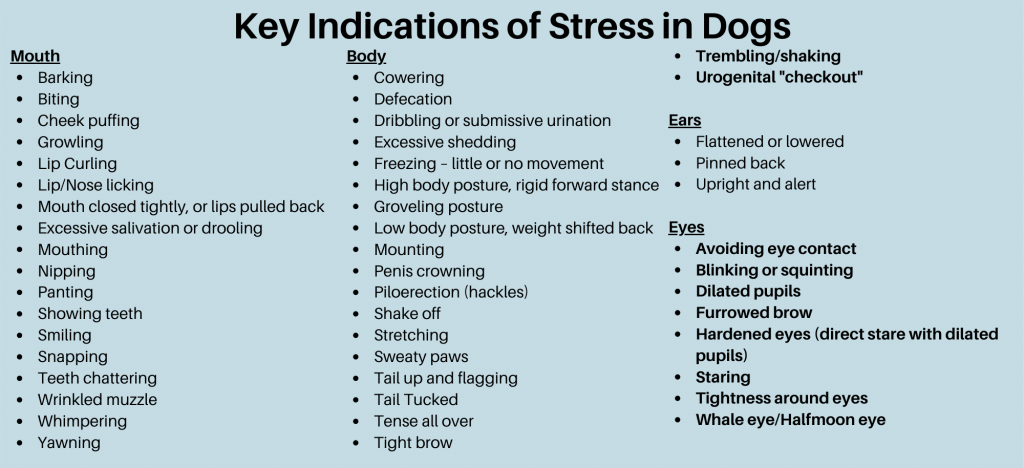
As described by Norwegian ethologist and dog behaviorist Turid Rugaas (2013), calming signals are very subtle changes in a dog’s body that suggest building stress. These signals are used in an attempt to diffuse conflict before it happens. A calming signal is a polite request to another dog to change its behavior and, therefore, prevent any dispute from occurring. Dogs use calming signals to communicate with us as well.
Two of the calming signals we see frequently are yawning and licking of the nose. The dog in the picture demonstrates both “averting of the eyes” and a “nose lick.” Other signs that can be calming signals are: the turn away, a softening of the eyes (squinting), averting the eyes, freezing, play bow, sitting down, lying down, sniffing, scratching, and splitting. I recommend that every pet parent and every pet care professional read at least one book on canine body language (See Recommended Resources for more information).
nose. The dog in the picture demonstrates both “averting of the eyes” and a “nose lick.” Other signs that can be calming signals are: the turn away, a softening of the eyes (squinting), averting the eyes, freezing, play bow, sitting down, lying down, sniffing, scratching, and splitting. I recommend that every pet parent and every pet care professional read at least one book on canine body language (See Recommended Resources for more information).
The Stress Escalation Ladder
Stress and the dog’s arousal happen on a continuum. Some of the signs of stress start appearing at very low levels of arousal. As the arousal level continues to rise, it may result in growling, showing of teeth, lunging, and biting at the most extreme levels. It is important to remember that arousal levels increase with positive stress (eustress) and negative stress (distress). Remember, it can take 24 to 72 hours for those levels to return to normal. A dog that is ramped up and highly aroused in play is also more likely to bite and lose its bite inhibition.
extreme levels. It is important to remember that arousal levels increase with positive stress (eustress) and negative stress (distress). Remember, it can take 24 to 72 hours for those levels to return to normal. A dog that is ramped up and highly aroused in play is also more likely to bite and lose its bite inhibition.
The image to the right reflects my interpretation of the Stress Escalation Ladder first described by Turid Rugaas. It illustrates the signs seen at various levels of arousal. It should always be our goal to keep the dog out of the yellow and red zones. I encourage every pet parent to recognize the signals that occur in the green zone, so they help their dog by getting them out of a stressful situation before it gets out of control.
Reducing Stress in Dogs
To reduce our dogs’ stress, we first need to understand it. Then, once we have identified the cause, there are many approaches to eliminating the stress.
The easiest way to deal with a dog under stress is usually management — removing the dog from the situation/context where the stress occurs. While this does not solve the problem, it is a temporary fix that will make the dog feel better. If this is a context/situation the dog will need to be exposed to in the future, it is advisable to work with a qualified behavior consultant or veterinary behaviorist to help the dog live in this context without experiencing stress. Behavioral medications may be necessary. Few people successfully resolve serious behavior issues on their own and, in my professional opinion, often make the problem worse. A dog chronically experiencing high levels of eustress or distress is not healthy and may be suffering. My recommendation is that such dogs need to be seen by a veterinary behaviorist.
A non-veterinary professional behavior consultant will always recommend that guardians discuss their dog’s behavioral issues with their veterinarian. Pain and other medical conditions can cause behavioral problems, and they need to be addressed first. In addition, in many parts of the world, tick-borne diseases are becoming more prevalent. These can cause behavioral/mental health symptoms in people (altered mental states, anorexia, anxiety, confusion, depression, fatigue, malaise, etc. ). Therefore, dogs with behavioral issues and tick-borne diseases may require treatment for those diseases as the initial step.
A behavior consultant will consider several methods to help your dog deal with their stress. Typically this will almost always include a behavior modification protocol (i.e., a specialized program for the dog’s specific situation) and management strategies to keep the dog out of stressful situations.
For many reasons, a training class is seldom recommended for a dog with stress-based issues such as anxiety or aggression. Behavior issues are often the result of an extreme emotional response. During such a response, the dog’s brain is not open to learning, and training does not change a dog’s emotions.
Teaching a dog to sit, down, stay, etc., will not change the way they feel. Asking a dog to sit in the presence of something that causes them to react may make them more fearful. Lastly, if a dog is reactive towards other dogs or people, putting them in a class where they will encounter those triggers would be highly counter-productive. A behavior modification program is all about changing a  dog’s emotional response to what makes them fearful or angry. (Note: A veterinary behaviorist may also determine whether drug therapy is necessary.)
dog’s emotional response to what makes them fearful or angry. (Note: A veterinary behaviorist may also determine whether drug therapy is necessary.)
Stress can make us feel miserable, and it can have the same effect on our dogs. For guardians who have a dog living under stress, I recommend they take steps to help them as soon as possible.
Take time to relax and destress with your dog. You will both benefit.
Recommended Resources
Animal Welfare – Assessing Pets’ Welfare Using Brambell’s Five Freedoms – http://bit.ly/Brambells-APDT2014
Do I Need a Dog Trainer or a “Behaviorist”? – http://bit.ly/WWM-Trainer-Behaviorist
Dominance: Reality or Myth – http://bit.ly/Dominance-RealityorMyth
Helping Your Dog Thrive with Brambell’s Five Freedoms – http://bit.ly/Brambell-1thru5-PDF
Help! My Dog is Aggressive, Reactive, Fearful, Anxious, etc. – What do I do? – WWM – APR2017 – http://bit.ly/HelpDogAggx
How Can I Tell When My Dog Is Anxious or Fearful? – http://bit.ly/DogsSignsofFear
How to Choose a Dog Trainer – http://bit.ly/HowToChooseADogTrainer
Introduction to Canine Communication – http://bit.ly/CanineComm
Understanding Behavior; Why It Matters – http://bit.ly/AnimalWelfare-Behavior
Management of An Aggressive, Fearful or Reactive Dog – http://bit.ly/BhxManagement
Puppy Socialization and Habituation – http://bit.ly/SocializationPuppy
Reward Based Training versus Aversives – http://bit.ly/RewardVSAversive
What Is A Pet Behavior Consultant? – http://bit.ly/WhatIsPetBhxConsulting
What Is Dog Training – http://bit.ly/WhatIsDogTraining
Your Pet’s Behavioral Health Is As Important As Their Physical Well-Being: The New AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines – http://bit.ly/WWM_AAHA_Bhx
Understanding, Identifying, and Coping with Canine Stress – https://bit.ly/WfMw-09OCT21-CanineStress
Canine Behavior: Myths and Facts – http://bit.ly/WfMwK9Bhx-26MAR16
Pet Behavior, Vets & The AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines with Dr. Dave Cloutier – http://bit.ly/WfMw-AAHA-Guidelines-13MAR16
The Dominance and Alpha Myth (2010) – http://bit.ly/WfMw-Dominance-2010
Other Online Resources
American Animal Hospital Association (2015.) AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines – https://www.aaha.org/aaha-guidelines/behavior-management/behavior-management-home/
BCSPCA. (2016, June 28). Tip Tuesday: Tips for dealing with dog reactivity – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j1J8uuJi0Ys
Garrod, D. (2019, November). Stress Matters. BARKS from the Guild (39) 36-39 – https://issuu.com/petprofessionalguild/docs/bftg_november_2019_online_edition_x_opt/36
Pet Professional Guild Finding A Professional (2020) – https://www.petprofessionalguild.com/Zip-Code-Search
Pet Professional Guild Guiding Principles (2012) – https://www.petprofessionalguild.com/Guiding-Principles
Pet Professional Guild Position Statements (2012-2019) – https://www.petprofessionalguild.com/Position-Statements
Turid Rugaas – Calming Signals – The Art of Survival (2013) – http://en.turid-rugaas.no/calming-signals—the-art-of-survival.html
 Books
Books
Brambell, R. (1965). Report of the technical committee to enquire into the welfare of animals kept under intensive livestock husbandry systems. London, UK: Her Majesty’s Stationery Office.
Chin, L. (2020). Doggie Language: A Dog Lover’s Guide to Understanding Your Best Friend. Chichester, UK: Summersdale Publishers
O’Heare, J. (2005). Canine Neuropsychology, 3rd edn. Ottawa, ON: DogPsych
Rugaas, T. (2005). On Talking Terms with Dogs: Calming Signals, 2nd edn. Wenatchee, WA: Dogwise
Strong, V. (1999). The Dog’s Brain — A Simple Guide. Windsor, UK: Alpha Publishing
Tudge, N. (2017). A Kids’ Comprehensive Guide to Speaking Dog! n.p.: Doggone Safe
________________________________________________________________________
Don Hanson is the co-owner of the Green Acres Kennel Shop ( greenacreskennel.com ) in Bangor, Maine, where he has been helping people with their pets since 1995. He is also the founder of ForceFreePets.com, an online educational resource for people with dogs and cats. Don is a Bach Foundation Registered Animal Practitioner (BFRAP), Certified Dog Behavior Consultant (CDBC), Associate Certified Cat Behavior Consultant (ACCBC), and a Certified Professional Dog Trainer (CPDT-KA). He is a member of the Pet Professional Guild (PPG). Don serves on the PPG Board of Directors and Steering Committee. In addition, he chairs the Advocacy Committee and The Shock-Free Coalition ( shockfree.org ). Don produces and co-hosts a weekly radio show and podcast, The Woof Meow Show, that airs on Z62 Retro Radio WZON (AM620) and WKIT 103.3-HD3 and is streamed at http://bit.ly/AM620-WZON every Saturday at 9 AM. Podcasts of the show are available at http://bit.ly/WfMwPodcasts/, the Apple Podcast app, and Don’s blog: www.words-woofs-meows.com. The opinions in this post are those of Don Hanson.
©17NOV21, Donald J. Hanson, All Rights Reserved <Click for Copyright and Use Policy>