This post is a handout for my presentation Pet Behavior as an Essential Component to Holistic Wellness given on Saturday, October 29th as part of Green Acres Kennel Shop’s fundraiser for The Green Gem Holistic Healing Oasis.
What is behavior? The Merriam-Webster online dictionary defines behavior as:
- the way a person or animal acts or behaves
- anything that an organism does involving action and response to stimulation
In August of 2015, the American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) addressed  the issue of behavior problems in pets with the publication of the AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines. This groundbreaking document reports that “Behavioral problems affect more dogs and cats than any other medical condition and are one of the most common causes of euthanasia, relinquishment, or abandonment of pets.” The report recommends that a behavioral wellness assessment should be part of every pet’s visit to the vet.
the issue of behavior problems in pets with the publication of the AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines. This groundbreaking document reports that “Behavioral problems affect more dogs and cats than any other medical condition and are one of the most common causes of euthanasia, relinquishment, or abandonment of pets.” The report recommends that a behavioral wellness assessment should be part of every pet’s visit to the vet.
The task force that wrote the AAHA Guidelines also looked at the question “Why have behavior issues become the number one issue for our pets?” According to the AAHA guidelines, it is because of:
- “Mistaken or misinformed beliefs…..” about canine behavior held by Breeders, Rescues and Shelters, Pet Care Professionals (Boarding Kennels and Daycares, Dog Trainers, Dog Walkers, Groomers, Pet Sitters, and Veterinarians), and Pet Owners
- The Use of Aversive Training Techniques
While not cited in the guidelines, studies suggest only 5% of dog owners ever attend a dog training class, and I suspect that also plays a factor in the frequency of behavior problems. A well-designed dog training class will cover much more than just how to train the dog. Our classes at Green Acres discuss husbandry issues, health and wellness, ethology, animal learning, and normal and abnormal behaviors. As a Certified Dog Behavior Consultant and Certified Professional Dog Trainer, I work with clients on both training and behavioral issues. Most of the clients that I see for behavioral issues did not take any dog training classes and may not have spent any time training the dog. I see very few clients for behavioral matters when the dogs and their people have been through at least one training class taught by a professional.
 The AAHA Guidelines suggest that the some of the “knowledge” we have about pet behavior may be more myth than fact while some of it is just plain erroneous. This antiquated mythology may be detrimental to our pet’s well-being and our relationship with our pet.
The AAHA Guidelines suggest that the some of the “knowledge” we have about pet behavior may be more myth than fact while some of it is just plain erroneous. This antiquated mythology may be detrimental to our pet’s well-being and our relationship with our pet.
So, let’s look at where people acquire knowledge about their pets. When I ask people this question, typical responses include; books, the breeder, a dog trainer, a family member, a friend, the internet, the shelter or rescue, or my veterinarian.
Not typically mentioned in the list is the societal influence of what we have  learned about pets, especially dogs, through the mass media. Many of us had our first exposure to dogs through characters like Lassie, Rin Tin Tin, Eddie, and Wishbone. We were probably exposed to these fictional dogs through TV shows, movies, books and sometimes all of the above. However, whether it was a book, movie, television show or comic book, it was a marvelous, heart-wrenching piece of fiction. Did it causes us to like dogs? Most likely it did, however, what these stories tell us about dog behavior is not real. As for cats, there is not as much “hero worship” in movies, books, and TV. When cats are portrayed in a movie, they are often the villain.
learned about pets, especially dogs, through the mass media. Many of us had our first exposure to dogs through characters like Lassie, Rin Tin Tin, Eddie, and Wishbone. We were probably exposed to these fictional dogs through TV shows, movies, books and sometimes all of the above. However, whether it was a book, movie, television show or comic book, it was a marvelous, heart-wrenching piece of fiction. Did it causes us to like dogs? Most likely it did, however, what these stories tell us about dog behavior is not real. As for cats, there is not as much “hero worship” in movies, books, and TV. When cats are portrayed in a movie, they are often the villain.
 Personally, much of what I first learned about dogs was based on these two popular books written back in the 70’s. When we brought our Cairn Terrier puppy home, we purchased copies of How To Be Your Dog’s Best Friend by the Monks of New Skete and Mother Knows Best by Carol Lea Benjamin. These were two of the most highly recommended books at the time, and both authors took the position that the dog is a descendant of a wolf and that we as its “parent” should teach it, or train it, just as a mother wolf would teach or train their offspring. Sadly, that often involved lots of intimidation, fear, and pain. Even sadder, these recommendations were not made based on any sound science. To this day I regret how following the recommendations in these books damaged the relationship between Gus and me. I cannot recommend these two books under any circumstances, expect as examples of what not to do.
Personally, much of what I first learned about dogs was based on these two popular books written back in the 70’s. When we brought our Cairn Terrier puppy home, we purchased copies of How To Be Your Dog’s Best Friend by the Monks of New Skete and Mother Knows Best by Carol Lea Benjamin. These were two of the most highly recommended books at the time, and both authors took the position that the dog is a descendant of a wolf and that we as its “parent” should teach it, or train it, just as a mother wolf would teach or train their offspring. Sadly, that often involved lots of intimidation, fear, and pain. Even sadder, these recommendations were not made based on any sound science. To this day I regret how following the recommendations in these books damaged the relationship between Gus and me. I cannot recommend these two books under any circumstances, expect as examples of what not to do.
I am pleased to say that there are now many books that I can recommend. They  are based on sound science and respect for dogs. Five books that I believe belong in every dog aficionados library are: On Talking Terms with Dogs: Calming Signals by Turid Rugaas, Dog Sense by John Bradshaw, The Other End of the Leash by Patricia McConnell, Ph.D, For the Love of A Dog by Patricia McConnell, Ph.D, and Dogs by Lorna Coppinger and Raymond Coppinger. My training colleagues will probably want to know why I have not included a training specific book in my recommendations. My answer is that basic training information will typically be provided by any professional trainer teaching private or group classes and I believe that pet parents/owners should take their dog to classes taught by professionals if they want the best for their dogs. However, for those that want a book on the topic, I recommend The Power of Positive Dog Training by Pat Miller.
are based on sound science and respect for dogs. Five books that I believe belong in every dog aficionados library are: On Talking Terms with Dogs: Calming Signals by Turid Rugaas, Dog Sense by John Bradshaw, The Other End of the Leash by Patricia McConnell, Ph.D, For the Love of A Dog by Patricia McConnell, Ph.D, and Dogs by Lorna Coppinger and Raymond Coppinger. My training colleagues will probably want to know why I have not included a training specific book in my recommendations. My answer is that basic training information will typically be provided by any professional trainer teaching private or group classes and I believe that pet parents/owners should take their dog to classes taught by professionals if they want the best for their dogs. However, for those that want a book on the topic, I recommend The Power of Positive Dog Training by Pat Miller.
 I have not forgotten cats. Unfortunately, cats have been studied much less than dogs and have typically been easier to acclimate into our lives. As a result, not as much as been written about them, especially their behavior. However, if you ask me to recommend a book on cats, the book I recommend will be Cat Sense by John Bradshaw.
I have not forgotten cats. Unfortunately, cats have been studied much less than dogs and have typically been easier to acclimate into our lives. As a result, not as much as been written about them, especially their behavior. However, if you ask me to recommend a book on cats, the book I recommend will be Cat Sense by John Bradshaw.
 Family members, friends and co-workers are often listed as a source of information about pets, often because they have had pets themselves. Some of these folks keep up with the latest information, but often they take the approach that is expressed in this slide; “I have had pets for over 40 years, and this is the way we have always done it!” implying there is no need to change. Since this person is often an authority figure in our eyes, we tend to follow their advice blindly. Recently I had a client tell me that their boss had suggested that they take a switch to their dog when the dog was whining. Even sadder is that I still occasionally have clients tell me that their breeder or even a member of their veterinary team has recommended hitting the dog with a newspaper for urinating in the house. It takes a long time for erroneous information and bad ideas to go away, so be a critical thinker when people suggest something and do not feel compelled to follow their advice.
Family members, friends and co-workers are often listed as a source of information about pets, often because they have had pets themselves. Some of these folks keep up with the latest information, but often they take the approach that is expressed in this slide; “I have had pets for over 40 years, and this is the way we have always done it!” implying there is no need to change. Since this person is often an authority figure in our eyes, we tend to follow their advice blindly. Recently I had a client tell me that their boss had suggested that they take a switch to their dog when the dog was whining. Even sadder is that I still occasionally have clients tell me that their breeder or even a member of their veterinary team has recommended hitting the dog with a newspaper for urinating in the house. It takes a long time for erroneous information and bad ideas to go away, so be a critical thinker when people suggest something and do not feel compelled to follow their advice.
 Today, many people look to television, “Reality TV” in particular, for information. I am not sure why they make this choice, other than “it is easy” and that it is also allegedly entertaining. The fact that it appears under the auspices of National Geographic also frankly gives it an aura of credibility that is not deserved. As I address some of the specific harmful myths about dog behavior still being perpetuated, you will find that these are the things people are “learning” on this particular show.
Today, many people look to television, “Reality TV” in particular, for information. I am not sure why they make this choice, other than “it is easy” and that it is also allegedly entertaining. The fact that it appears under the auspices of National Geographic also frankly gives it an aura of credibility that is not deserved. As I address some of the specific harmful myths about dog behavior still being perpetuated, you will find that these are the things people are “learning” on this particular show.
Just to be fair, I am not a fan of most reality TV shows. They often present complex behavioral issues and then show them being “fixed” in a week’s time. I get it. People want an easy fix. Easy fixes are seldom reality with behavioral problems. When these same shows recommend things that the AAHA Guidelines specifically cite as the reason for behavior problems, I am going to advise you to turn them off.
Last on my list is the internet. In the last twenty years, the internet has become  the first choice of information for many. Earlier in this article, I shared a definition from the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. I love this easy access to valuable information, but as the State Farm Insurance commercial illustrated in this slide has demonstrated so well is that not all information on the internet is reliable information. Just because it is on the internet does not mean that it is true. Just as the internet has made information more accessible, it has also made the dissemination of inaccurate information easier. Be a critical thinker.
the first choice of information for many. Earlier in this article, I shared a definition from the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. I love this easy access to valuable information, but as the State Farm Insurance commercial illustrated in this slide has demonstrated so well is that not all information on the internet is reliable information. Just because it is on the internet does not mean that it is true. Just as the internet has made information more accessible, it has also made the dissemination of inaccurate information easier. Be a critical thinker.
I am now going to address some of the most egregious myths about both dog and cat behavior. This will not be a complete discussion of the topic but will be a start. For those of you that want to know more (Good for you!!) I will list recommended resources at the end of this article where you can do just that.
This idea that dogs are the same as wolves is the big lie on which many of these  other myths have been based. The fact is the wolf, coyote, and the domestic dog did have a common ancestor 9,000 to 34,000 years ago. However, that ancestor has been extinct for centuries, and the wolf, coyote, and domestic dog have each evolved to fit a different ecological niche. While biologically they can interbreed, behaviorally they are very different.
other myths have been based. The fact is the wolf, coyote, and the domestic dog did have a common ancestor 9,000 to 34,000 years ago. However, that ancestor has been extinct for centuries, and the wolf, coyote, and domestic dog have each evolved to fit a different ecological niche. While biologically they can interbreed, behaviorally they are very different.
 Wolves do everything they can to avoid humans, having an almost instinctual aversion to us. This is easy to understand since humans have been trying to exterminate wolves as a species for thousands of years. At the same time, most dogs are drawn to humans as long as we treat them kindly. This attraction has much to do with how the domestic dog evolved. The best theory on the domestication of the dog was developed by Lorna and Ray Coppinger and is discussed in their book Dogs. The domestic dogs came about around the same time that humans shed their hunter-gather ways and settled into villages and developed agriculture. Since we were no longer on the move, we could not just walk away from all of the refuse our wasteful species creates, so some early person invented the concept of the village dump. The least fearful wolves noted this development and started feasting at the dump as the humans slept. Why go out on a dangerous hunt where you might not find something or could get maimed or killed, when you could feast on the waste of humankind. Over thousands of years these wolves evolved into the domestic dog, basically domesticating themselves. In fact, feral populations of dogs can still be found in many places throughout the world, often around the city dump.
Wolves do everything they can to avoid humans, having an almost instinctual aversion to us. This is easy to understand since humans have been trying to exterminate wolves as a species for thousands of years. At the same time, most dogs are drawn to humans as long as we treat them kindly. This attraction has much to do with how the domestic dog evolved. The best theory on the domestication of the dog was developed by Lorna and Ray Coppinger and is discussed in their book Dogs. The domestic dogs came about around the same time that humans shed their hunter-gather ways and settled into villages and developed agriculture. Since we were no longer on the move, we could not just walk away from all of the refuse our wasteful species creates, so some early person invented the concept of the village dump. The least fearful wolves noted this development and started feasting at the dump as the humans slept. Why go out on a dangerous hunt where you might not find something or could get maimed or killed, when you could feast on the waste of humankind. Over thousands of years these wolves evolved into the domestic dog, basically domesticating themselves. In fact, feral populations of dogs can still be found in many places throughout the world, often around the city dump.
Since many people erroneously believed that dogs are wolves, they also assumed that dogs were pack animals. A wolf pack consists of a breeding pair of wolves and often multiple generations of offspring, working together as a family, to survive and to pass on their genes. Both parents, as well as older siblings, play a role in raising the young. For male domestic dogs, procreation is all about a one night stand. In feral groups of dogs, the male plays no role in raising the young and usually is not seen again. A group of dogs does not resemble the tight-knit relationship of a pack in any way.
that dogs were pack animals. A wolf pack consists of a breeding pair of wolves and often multiple generations of offspring, working together as a family, to survive and to pass on their genes. Both parents, as well as older siblings, play a role in raising the young. For male domestic dogs, procreation is all about a one night stand. In feral groups of dogs, the male plays no role in raising the young and usually is not seen again. A group of dogs does not resemble the tight-knit relationship of a pack in any way.
Dogs are social animals, and when they live ferally, they may form loose,  temporary associations with a few other dogs. Two or more dogs may occasionally hang out together, but they do NOT live in close family groups like wolves. While many of us have multiple dogs living in our homes, they also do not have the tight-knit family connection and evolutionary drive to keep the family genes alive. That may be one of the reasons it is not always possible to get a group of dogs to live together peacefully. I have lived with a variety of multiple dog scenarios, and I can only recall two dogs that enjoyed one another’s company on a regular basis.
temporary associations with a few other dogs. Two or more dogs may occasionally hang out together, but they do NOT live in close family groups like wolves. While many of us have multiple dogs living in our homes, they also do not have the tight-knit family connection and evolutionary drive to keep the family genes alive. That may be one of the reasons it is not always possible to get a group of dogs to live together peacefully. I have lived with a variety of multiple dog scenarios, and I can only recall two dogs that enjoyed one another’s company on a regular basis.
 Also out of all this wolf nonsense came the doctrinaire belief that to keep order and to be able to train my dogs that one must be dominant, or that one must be the “Alpha.” Dominance is not only an erroneous understanding of the dog-human relationship, but it is also counterproductive to a harmonious relationship with our dog. Trying to be dominant may cause aggression.
Also out of all this wolf nonsense came the doctrinaire belief that to keep order and to be able to train my dogs that one must be dominant, or that one must be the “Alpha.” Dominance is not only an erroneous understanding of the dog-human relationship, but it is also counterproductive to a harmonious relationship with our dog. Trying to be dominant may cause aggression.
The two books I mentioned previously, How To Be Your Dog’s Best Friend by the Monks of New Skete and Mother Knows Best by Carol Lea Benjamin, bought into the Alpha concept big time. In my opinion, this is the myth that has done the greatest harm to dogs. The idea that we must be the Alpha is responsible for training methods and tools based on force, pain, intimidation, and fear. Which is why, in the AAHA guidelines, the American Animal Hospital Association specifically tells veterinarians to avoid recommending clients to trainers that use the dominance model of training.
Most people get a dog to be their companion. Why would we want to use fear, force, and pain to nurture a relationship with a friend?
If you want detailed information on the dominance myth, with references to the scientific literature, read http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2015/06/20/dog-behavior-dominance-reality-or-myth/
Directly associated with the idea that one must be dominant over a dog was the  promotion of aversive tools and methods designed to compel and intimidate the dog. These tools included; squirt bottles, choke collars, prong collars, citronella collars, shock collars, the Monks of New Skete’s infamous alpha roll and others. Some trainers and books even went so far as to recommend beating a dog or even almost drowning a dog for digging.
promotion of aversive tools and methods designed to compel and intimidate the dog. These tools included; squirt bottles, choke collars, prong collars, citronella collars, shock collars, the Monks of New Skete’s infamous alpha roll and others. Some trainers and books even went so far as to recommend beating a dog or even almost drowning a dog for digging.
 The 2015 AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines opposes the use of aversives.
The 2015 AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines opposes the use of aversives.
“This Task Force opposes training methods that use aversive techniques. Aversive training has been associated with detrimental effects on the human–animal bond, problem solving ability, and the physical and behavioral health of the patient. It causes problem behaviors in normal animals and hastens progression of behavioral disorders in distressed animals. Aversive techniques are especially injurious to fearful and aggressive patients and often suppress signals of impending aggression, rendering any aggressive dog more dangerous.
Aversive techniques include prong (pinch) or choke collars, cattle prods, alpha rolls, dominance downs, electronic shock collars, lunge whips, starving or withholding food, entrapment, and beating. None of those tools and methods should be used to either teach or alter behavior.”
The fact is, dogs respond well to a kind and trustworthy leader skilled in the  science of reward-based training. Even children, with adult supervision, can take part in training when food rewards are used.
science of reward-based training. Even children, with adult supervision, can take part in training when food rewards are used.
For reasons known only to them, the Monks of New Skete stressed that a dog should work just to please us and not for food. The fact is, rewards work very well for training almost all species of animals. When it comes to dogs, food has more value as a reinforcer than either praise or touch, as confirmed by a study published in the Journal of Experimental Analysis of Behavior in July of 2012.
 I hear students say it, I see it all over the internet, and I get why people might want to believe that dogs naturally want to please us. Unfortunately, it is just not true. Put your logical hats on and ask yourself this; “If dogs naturally want to please us, why are behavior problems the number one problem facing dogs and dog owners? Why do dog trainers and dog behavior consultants even exist? The fact is, dogs are like every other living thing on this planet, they do certain things because it benefits their existence.
I hear students say it, I see it all over the internet, and I get why people might want to believe that dogs naturally want to please us. Unfortunately, it is just not true. Put your logical hats on and ask yourself this; “If dogs naturally want to please us, why are behavior problems the number one problem facing dogs and dog owners? Why do dog trainers and dog behavior consultants even exist? The fact is, dogs are like every other living thing on this planet, they do certain things because it benefits their existence.
Now I will agree that most dogs, not all, have an affinity for people. They enjoy  our company, seek us out, and have an uncanny ability to read us and behave accordingly. In fact, studies suggest that dogs read us better than wolves, the species closest to the dog, and chimpanzees, the species closest to humans. This ability to read humans probably has much to do with how dogs evolved, hanging around humans and observing our behaviors and signals that indicate when we are “safe” versus “dangerous.”
our company, seek us out, and have an uncanny ability to read us and behave accordingly. In fact, studies suggest that dogs read us better than wolves, the species closest to the dog, and chimpanzees, the species closest to humans. This ability to read humans probably has much to do with how dogs evolved, hanging around humans and observing our behaviors and signals that indicate when we are “safe” versus “dangerous.”
There are many other myths about canine behavior, but due to our limited time I have only covered some of them today. Subscribe to my blog http://www.words-woofs-meows.com and you will be notified when I post new articles.
 So what about cats? I think we would all agree that they do have behavioral issues. Like any animal, they can be afraid, angry, anxious and depressed. For whatever reasons people are more likely to live with a cat with behavioral issues than they are with a dog. Also, cats have been studied much less than dogs, so we do not know as much about them. However, there are some misconceptions about feline behavior that I would like to address today.
So what about cats? I think we would all agree that they do have behavioral issues. Like any animal, they can be afraid, angry, anxious and depressed. For whatever reasons people are more likely to live with a cat with behavioral issues than they are with a dog. Also, cats have been studied much less than dogs, so we do not know as much about them. However, there are some misconceptions about feline behavior that I would like to address today.
Many see the “domestic” cat as being independent to the point of being anti- social. Compared to most dogs, cats are less gregarious, but there are some very good reasons for that behavior. Like puppies, kittens have a critical socialization period where they are more likely to be accepting of novel stimuli; however, this period is over before a kitten is eight weeks of age. Unless the breeder, humane society, or person with a box full of kittens has been actively and appropriately socializing those kittens, as adult cats they will most likely be fearful or at least suspicious of anything that they have not experienced before eight weeks of age.
social. Compared to most dogs, cats are less gregarious, but there are some very good reasons for that behavior. Like puppies, kittens have a critical socialization period where they are more likely to be accepting of novel stimuli; however, this period is over before a kitten is eight weeks of age. Unless the breeder, humane society, or person with a box full of kittens has been actively and appropriately socializing those kittens, as adult cats they will most likely be fearful or at least suspicious of anything that they have not experienced before eight weeks of age.
We must also recognize that cats have been persecuted by humans for centuries, and I suspect we all have at least a few people in our lives who have stated: “I hate cats!”
 Lastly, although we consider the cat to be domesticated, animal scientists would suggest that is not the case. Feral colonies of cats are abundant throughout the world, and they survive well on their own. Cats are just not as dependent on us as dogs, which is why they are classified as commensalists; a species that derives benefits from living with another species but does not cause it harm.
Lastly, although we consider the cat to be domesticated, animal scientists would suggest that is not the case. Feral colonies of cats are abundant throughout the world, and they survive well on their own. Cats are just not as dependent on us as dogs, which is why they are classified as commensalists; a species that derives benefits from living with another species but does not cause it harm.
Unlike their wild ancestor’s, cats are highly social with one another, and female  cats that are related will often live in social groups and may even raise one another’s young. However, males are excluded from these groups as they would typically kill the kittens if given the opportunity. As a result, the males live in less affiliated social groups, away from the females.
cats that are related will often live in social groups and may even raise one another’s young. However, males are excluded from these groups as they would typically kill the kittens if given the opportunity. As a result, the males live in less affiliated social groups, away from the females.
 Cats are very territorial, both outdoors and indoors and with known and unknown cats. Litter box issues, the most common behavioral complaint with cats, can be caused by a cat guarding and denying access to the litterbox or a new outdoor cat moving into the neighborhood. Typical behavioral responses to territorial issues include; fighting, urine spraying, urine marking, fecal marking, scratching, and scent marking.
Cats are very territorial, both outdoors and indoors and with known and unknown cats. Litter box issues, the most common behavioral complaint with cats, can be caused by a cat guarding and denying access to the litterbox or a new outdoor cat moving into the neighborhood. Typical behavioral responses to territorial issues include; fighting, urine spraying, urine marking, fecal marking, scratching, and scent marking.
Most cats will live longer if they are kept indoors and not allowed to go outside;  however, a cat who is not allowed to go outdoors is not necessarily living a better life than those who live indoors and out. The dog and cat are both predatory creatures, but the cat, because it is less domesticated, typically has stronger predatory instincts than most dogs. They still have a very instinctual need to hunt and if given the option, would be highly mobile, traveling as much as six miles per day.
however, a cat who is not allowed to go outdoors is not necessarily living a better life than those who live indoors and out. The dog and cat are both predatory creatures, but the cat, because it is less domesticated, typically has stronger predatory instincts than most dogs. They still have a very instinctual need to hunt and if given the option, would be highly mobile, traveling as much as six miles per day.
Brambell’s five freedoms describe the basic needs we must meet to ensure an animals basic welfare, and one of those freedoms is the ability to express normal behaviors. Hunting, killing, and consuming small rodents is a normal behavior for a cat. When we deny that behavior, it may cause other behavioral issues.
 Behavioral issues are usually driven by emotion. Whether your pet is displaying aggression, hyperactivity, fatigue, irritability, or a loss of interest in life, there will usually be an underlying emotion such as fear, anger, grief, frustration, or depression behind the behavior. Training, teaching a dog to sit or stay, does not typically change emotions and can, in fact, make a negative emotional response worse. For example, is your dog likely to feel better or worse if they are afraid of men in beards and you make your dog sit and stay next to you while you have a conversation with a bearded man? I suspect they will feel trapped and more fearful.
Behavioral issues are usually driven by emotion. Whether your pet is displaying aggression, hyperactivity, fatigue, irritability, or a loss of interest in life, there will usually be an underlying emotion such as fear, anger, grief, frustration, or depression behind the behavior. Training, teaching a dog to sit or stay, does not typically change emotions and can, in fact, make a negative emotional response worse. For example, is your dog likely to feel better or worse if they are afraid of men in beards and you make your dog sit and stay next to you while you have a conversation with a bearded man? I suspect they will feel trapped and more fearful.
Now while you may believe that there is no reason for your dog to fear the bearded man, that DOES NOT MATTER! While your dog’s response may seem irrational to you, it is not irrational to them.
Some pet guardians insist that their pet MUST like all people. I understand why a  person may want that response, but is that a realistic expectation? If we are honest with ourselves, most of us would admit that we do not like and enjoy the company of every other human on the planet. Is it fair to ask that of our pets?
person may want that response, but is that a realistic expectation? If we are honest with ourselves, most of us would admit that we do not like and enjoy the company of every other human on the planet. Is it fair to ask that of our pets?
Equally problematic are the people who insist that they “love all animals” and that all animals love them. These folks then try to force their “love” on an animal and will not stop until you ask them to, and sometimes even then they continue. The fact is not all pets are going to like all people, and there is nothing we can do but to accept that.
What a wonderful world it would be if your dog liked all other dogs and all other dogs liked your dog. Moreover, it would be even better if all cats liked all cats, and dogs and cats all enjoyed one another’s company. While we are at it, let’s add mice and chickens to the dog and cat Kumbaya moment. Is this a realistic expectation? We all know that is not realistic.
 I have lived in a multi-pet household for over twenty years with a total of eight dogs and six cats. I had two dogs that, in my opinion, enjoyed one another’s company, two cats that had frequent positive social interactions, and I had a dog and a cat that had a “relationship.” However, in all those cases there were always times when the “friends” were not friends. In most cases, most of my pets had no interest in the other pets.
I have lived in a multi-pet household for over twenty years with a total of eight dogs and six cats. I had two dogs that, in my opinion, enjoyed one another’s company, two cats that had frequent positive social interactions, and I had a dog and a cat that had a “relationship.” However, in all those cases there were always times when the “friends” were not friends. In most cases, most of my pets had no interest in the other pets.
When we bring a pet into a home with existing pets, we cannot guarantee it will work out, and sometimes the kindest thing we can do is to rehome the newest pet. We introduced a new dog to our family that had to be rehomed because she was going to kill one of our other dogs.
I think it is great that people rescue pets; however, and each situation is different, I do believe that a home, and by “home” I mean more than the physical environment, has a maximum carrying capacity for pets. When you exceed that capacity, you start to see behavioral problems. My wife and I have intentionally downsized or furry family so that we can make sure each pet has the best life we can provide.
So, if you accept that your pet’s behavioral health is an essential component to  their overall health and wellness, what can you do? Since lack of knowledge or erroneous knowledge is a primary reason for behavioral issues with pets, continue to seek knowledge. Be open-minded and willing to let some of those old notions, like dominance, drift away. Be a critical thinker. Make sure what you are learning makes sense and feels right.
their overall health and wellness, what can you do? Since lack of knowledge or erroneous knowledge is a primary reason for behavioral issues with pets, continue to seek knowledge. Be open-minded and willing to let some of those old notions, like dominance, drift away. Be a critical thinker. Make sure what you are learning makes sense and feels right.
 If you have behavioral concerns with your pet, seek professional help early. The longer these problems continue, the longer they will take to resolve. The probability of satisfactorily changing a behavior also decreases the longer it occurs, as many of these undesirable behaviors are self-rewarding.
If you have behavioral concerns with your pet, seek professional help early. The longer these problems continue, the longer they will take to resolve. The probability of satisfactorily changing a behavior also decreases the longer it occurs, as many of these undesirable behaviors are self-rewarding.
Many behavioral problems can be the result of medical issues. Seek medical  advice from trained veterinary professionals to rule out medical issues first. If there is an underlying medical issue, a behavior specialist may be of limited help. Discuss your pet’s behavior, good or bad, with your veterinarian at EVERY visit. Changes in behavior can be an early indicator of other health issues.
advice from trained veterinary professionals to rule out medical issues first. If there is an underlying medical issue, a behavior specialist may be of limited help. Discuss your pet’s behavior, good or bad, with your veterinarian at EVERY visit. Changes in behavior can be an early indicator of other health issues.
Make sure that your veterinary team meets or exceeds the standards set in the American Animal Hospital Association AAHA 2015 Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines and that they will work with the behavioral professional you choose. Also, make sure that your veterinary team does not use or recommend aversives.
Avoid seeking veterinary advice from Google, breeders, family members, friends, or co-workers.
 Seek advice from trained behavioral professionals not Google, breeders, family members, friends, or co-workers. Pet training and behavioral consulting is an unregulated profession, so you need to choose your caregiver wisely. I only refer to those credentialed by the Pet Professional Guild (PPG) and the International Association of Animal Behavior Consultants (IAABC). Also, make sure that your behavioral consultant meets or exceeds the standards set in the Position Statements of The Pet Professional Guild (PPG) and the American Animal Hospital Association AAHA 2015 Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines.
Seek advice from trained behavioral professionals not Google, breeders, family members, friends, or co-workers. Pet training and behavioral consulting is an unregulated profession, so you need to choose your caregiver wisely. I only refer to those credentialed by the Pet Professional Guild (PPG) and the International Association of Animal Behavior Consultants (IAABC). Also, make sure that your behavioral consultant meets or exceeds the standards set in the Position Statements of The Pet Professional Guild (PPG) and the American Animal Hospital Association AAHA 2015 Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines.
Make sure that your behavioral consultant will work with the veterinary professional you choose and does not use or recommend aversives.
Reject the use of ANY and ALL aversives and choose professionals that do so as well.
Aversives may stop behavior temporarily, but they do not resolve the underlying  cause of the behavior nor do they teach the pet the behavior we want instead. Aversives impair learning and often cause the behavior to become worse. They can also damage the bond between you and your pet.
cause of the behavior nor do they teach the pet the behavior we want instead. Aversives impair learning and often cause the behavior to become worse. They can also damage the bond between you and your pet.
 As a Certified Professional Dog Trainer and Certified Dog Behavior Consultant I work with a wide variety of people and their dogs. They might seek out my advice on what to look for in a dog or enroll in one of our training classes to learn how to effectively and humanely train their dog in a fun manner. In some cases, they come to me because they need help with a dog with separation anxiety or aggression issues. In almost all of the latter cases, those dogs have had little or no training.
As a Certified Professional Dog Trainer and Certified Dog Behavior Consultant I work with a wide variety of people and their dogs. They might seek out my advice on what to look for in a dog or enroll in one of our training classes to learn how to effectively and humanely train their dog in a fun manner. In some cases, they come to me because they need help with a dog with separation anxiety or aggression issues. In almost all of the latter cases, those dogs have had little or no training.
If you get a dog, invest the time in taking them to at least a Puppy Headstart and Basic Manners training class. You will not regret it.
Thank you for your time today. If you have any questions, please feel free to call me at Green Acres Kennel Shop (207) 945-6841 or email me at donh@greenacreskennel.com
Recommended Resources
Articles on Don’s Blog (http://www.words-woofs-meows.com)
Dog Training – How science and reward-based training have pulled dog training out of the dark ages – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/04/21/dog-training-how-science-and-reward-based-training-have-pulled-dog-training-out-of-the-dark-ages/
A Rescue Dogs Perspective on Dog Training –http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/01/04/dog-training-a-rescue-dogs-perspective/
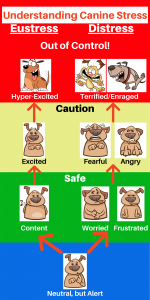
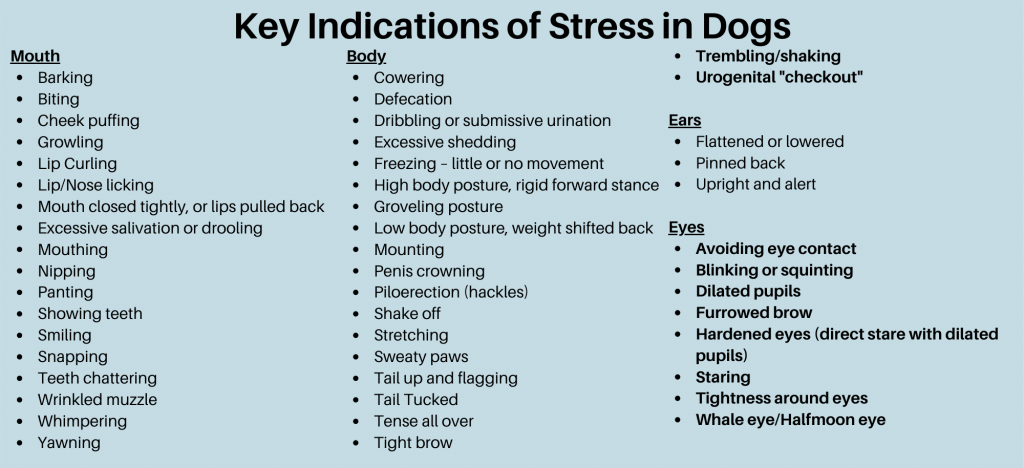
Canine Behavior – Understanding, Identifying, and Coping with Canine Stress –http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2015/11/01/canine-behavior-understanding-identifying-and-coping-with-canine-stress/
Dog Behavior – Dominance: Reality or Myth –http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2015/06/20/dog-behavior-dominance-reality-or-myth/
Dog Training: A Holistic Approach to Dog Training (Parts 1 & 2) –http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2015/02/01/dogs-dog-training-a-holistic-approach-to-dog-training-parts-1-2/
Dog Training – The Four Essentials For A Great Dog – Part 1 –http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/02/02/dog-training-the-four-essentials-for-a-great-dog-part-1-knowledge-relationship-management-training/
Dog Training – The Four Essentials For A Great Dog – Part 2 –http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/02/28/dog-training-the-four-essentials-for-a-great-dog-part-2/
Dog Training – What Is Clicker Training? –http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2007/02/01/dog-training-what-is-clicker-training/
Green Acres Kennel Shop Position Statement on Pet-Friendly, Force-Free Pet Care – http://www.greenacreskennel.com/boarding/what-is-pet-friendly
Green Acres Kennel Shop Position Statement on the Use of Dominance and Punishment for the Training and Behavior Modification of Dogs – http://www.greenacreskennel.com/training/position-on-the-use-of-dominance-and-punishment-for-the-training-and-behavior-modification-of-dogs
The Unintended Consequences of Shock Collars – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2013/08/05/dogs-the-unintended-consequences-of-shock-collar/
Podcasts from The Woof Meow Show (http://www.woofmeowshow.com)
<Click on the title to listen to the show>
Canine Behavior: Myths and Facts
The Four Essentials to A Great Dog
Dog Training Questions for Don and Kate with special guest host Dr. Mark Hanks – part 1
Dog Training Questions for Don and Kate with special guest host Dr. Mark Hanks – part 2
Dog Training Questions for Don and Kate with special guest host Dr. Mark Hanks – part 3
Books
On Talking Terms With Dogs: Calming Signals, Turid Rugaas, Dogwise Publishing, 2006, An excellent book on understanding a dog’s body language. Includes descriptions of how you can use your own body language to better communicate with your dog.
Dog Sense: How the New Science of Dog Behavior Can Make You A Better Friend to Your Pet, John Bradshaw, Basic Books, 2011,
The Other End of the Leash – Why We Do What We Do Around Dogs,Patricia B. McConnell, Ph.D, Ballantine Books, 2002, An information-packed, immensely readable book. In it you will learn how to have a better relationship with your dog through better communications. Dr. McConnell clearly explains the manners in which dogs and their people communicate.
For the Love of A Dog Understanding Emotion in You and Your Best Friend, Patricia B. McConnell, Ph.D, Ballantine Books, 2005, 2006, A superb review of emotions in both dogs and their people and how they bring us together and can rip us apart. Once again Dr. McConnell helps us to better understand our dogs and in doing so have the best possible relationship with them.
Dogs: A new Understanding of Canine Origin, Behavior and Evolution, Raymond and Lorna Coppinger, University of Chicago Press, 2001, An evolutionary biologist and dog lover, Coppinger outlines the likely process which resulted in the longstanding canine-human relationship.
Stress in Dogs, Martina Scholz and Clarissa von Reinhardt, Dogwise Publishing, 2007, This book outlines the physiology of stress in dogs, signs of stress, and how to make your dog’s life less stressful. It emphasizes that more activity and involvement in dog sports is often not the answer to reducing stress in dogs but can be a major contributing factor. This book is a must read for anyone with an anxious or hyper dog.
The Culture Clash, Jean Donaldson, James & Kenneth Publishers, 2005. An exciting book by an outstanding dog trainer and one of Don’s favorites. Donaldson makes a powerful case for thinking in terms of behavior modification rather than the older and more anthropomorphic dominance models of dog training. Includes an excellent section on operant conditioning. Winner of the Dog Writer Association of America’s “Best Behavior Book” award for 1997.
The Power of Positive Dog Training, Pat Miller, Howell Book House, 2001. I have been reading Pat Miller’s articles in the Whole Dog Journal for years and have loved everything she has written. She is a skilled and compassionate dog trainer who really knows how to communicate to dog owners through her writing. This book is a superb “basic dog book” for anyone with a dog, and I highly recommend it.
The Dog Whisperer, Paul Owens with Norma Eckroate, Adams Media Corp., 2007. This book emphasizes a compassionate, nonviolent approach to dog training. It offers great advice on building a relationship with your dog and shows you how to teach your dog all of the basics they need to be a great companion.
Don’t Shoot the Dog – The New Art of Teaching and Training (2nd edition), Karen Pryor, Bantam Books, 1999. A pioneering book using shaping to change behavior in animals – dogs, cats, even humans.
Training Your Cat, Dr. Kersti Seksel, Hyland House Publishing, 1999. Written by an Australian veterinarian, this book is an excellent primer on cat behavior, care and training. While many people think cats cannot be trained, this book demonstrates exactly how easy training a cat can be.
______________________________________________________________________________
Don Hanson is the co-owner of the Green Acres Kennel Shop (greenacreskennel.com) in Bangor. He is a Bach Foundation Registered Animal Practitioner (BFRAP), Certified Dog Behavior Consultant (CDBC), Associate Certified Cat Behavior Consultant (ACCBC) and a Certified Professional Dog Trainer (CPDT-KA). He produces and co- hosts a weekly radio show and podcast, The Woof Meow Show heard on The Pulse AM620 WZON and streamed at http://www.wzonradio.com/ every Saturday at 9 AM. A list of upcoming shows and podcasts of past shows can be found at www.woofmeowshow.com. Don also writes about pets at his blog: www.words-woofs-meows.com.
©26-Oct-16, Donald J. Hanson, All Rights Reserved <Click for Copyright and Use Policy)