< A version of this article was published in the April 2017 issue of Downeast Dog News>
< A version of this article was published in the April 2017 issue of Downeast Dog News>
< a short link to this article – http://bit.ly/HelpDogAggx >
< Updated 22MAY22 >
Step one – Know that you are not alone. I receive several calls per week from people that are concerned about how their dog is behaving towards them, other people, other dogs, other animals, or maybe some combination of things. Aggression, reactivity, fear, and anxiety are all on a continuum of behaviors and the primary reason I see dogs for behavior consultations. Fear is almost always a direct cause or a major factor in aggression and reactivity. Previously in this column, I have discussed the 2015 American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines which reported that “Behavioral problems affect more dogs and cats than any other medical condition and are one of the most common causes of euthanasia, relinquishment, or abandonment of pets.” You are not alone.
Aggression, reactivity, fear, and anxiety are all on a continuum of behaviors and the primary reason I see dogs for behavior consultations. Fear is almost always a direct cause or a major factor in aggression and reactivity. Previously in this column, I have discussed the 2015 American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines which reported that “Behavioral problems affect more dogs and cats than any other medical condition and are one of the most common causes of euthanasia, relinquishment, or abandonment of pets.” You are not alone.
Step two – Understand that your dog is not a “Bad Dog” nor are they giving you a hard time. A dog that is reacting is scared, in pain, or anxious. They are asking for your understanding and help. Getting mad at your dog and punishing them in any way will only increase their distress. < FMI – Potential Causes for Reactivity (Shyness, Anxiety, Fear, and Terror) in a Dog – https://bit.ly/Causes-Reactivity & Reactivity Misunderstood – https://bit.ly/ReactivityMisunderstood >
Step three – Act Now!! Accept that behavioral issues will not go away on their own nor will your dog outgrow them. Commit to act NOW! Understand that these matters are every bit as traumatic to your dog as they are to you. You are both suffering. Delaying action is only likely to make the resolution of these issues harder and in all probability take longer.
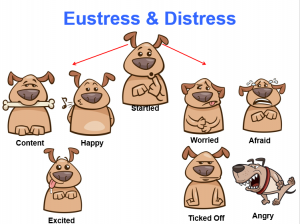
Step four – Learn to recognize the signs of fear in your dog and act to remove them from fearful situations. Most dogs communicate when they become nervous and afraid through their body language long before they vocalize or act. If you know these signs, you can get your dog out of a situation that will cause them to become more anxious. < FMI – How Can I Tell When My Dog Is Anxious or Fearful? – http://bit.ly/DogsSignsofFear > Dog Trainer Angelica Steinker Addresses why this is so important in her article Why Counterconditioning “Doesn’t Work. She explains that counterconditioning protocols typically fail due to user error. Due to ignorance and/or impatience, the people implementing the protocol often neglect to consider the keys to a successful counterconditioning protocol that Steinker outlines in her article. Her core message is the dog being counter conditioned MUST feel safe and relaxed. <FMI – https://barksfromtheguild.com/2021/11/11/why-counterconditioning-doesnt-work/? >
Step five – Stop the use of force, fear, and pain. Immediately stop the use of any and all aversives for the management and training of your dog. Common aversives include but are not limited to; prong, pinch, choke, or shock collars, alpha rolls, squirt bottles, and the entire dominance/alpha construct. Aversives impair our dog’s ability to learn, damage the human-dog bond and trust, and often result in an emotional outburst resulting in the same behavior problems you wish to resolve. For these reasons, the AAHA guidelines, The American Veterinary Society of Animal Behavior (AVSAB), and the Pet Professional Guild (PPG) categorically oppose the use of aversive techniques for the training and husbandry of a dog. < FMI – Dog Training – Reward Based Training versus Aversives – http://bit.ly/RewardVSAversive >
Step six – Manage Your Dog and Their Environment to Prevent the Behavior – If you have a dog that could potentially injure any other living thing, you have a moral and legal responsibility to prevent that from happening. It is also essential to understand that a dog that continues to behave aggressively does so because they are being rewarded for that behavior. While you may not be intentionally rewarding reactivity and aggression, the environment or the dog’s own internal reward mechanisms can act as a reinforcer. Every time this behavior is rewarded it becomes stronger and more likely. < FMI – Management of An Aggressive, Fearful or Reactive Dog – http://bit.ly/BhxManagement >
Step seven – Talk to your veterinarian or a veterinary behaviorist. If you have not already done so, make an appointment with your veterinarian to have a detailed discussion about your dog’s behavioral issues. Aggression can be caused by many medical problems. Pain, neurological disorders, tumors, tick-borne diseases, thyroid disease, other hormone-related problems, and even an adverse reaction to a vaccine can cause aggression. Any medical issues related to your dog’s behavior need to be identified and resolved if you wish the behavior to change.
A Veterinary Behaviorist is a veterinarian who has completed additional education and a residency specializing in animal behavior. These specialists have a comprehensive understanding of your animal. They are uniquely qualified to diagnose and treat all aspects of your pets, physical and mental health. Dr. Christine Calder is the only Veterinary Behaviorist practicing in Maine. I have included her contact information below as well as a link to an interview with her on my radio show/podcast, The Woof Meow Show.
Contact Info for Dr. Calder
Business: Calder Veterinary Behavior Services
Phone: (207) 298-4375
Email: reception@caldervbs.com
Website: www.caldervbs.com
Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/Christine-Calder-DVM-DACVB-Veterinary-Behaviorist-104864721012254/
More info on Dr. Calder from the January 2020 issue of Downeast Dog News – https://downeastdognews.villagesoup.com/p/what-is-a-veterinary-behaviorist/1846547
Podcast – Introducing Dr. Christine Calder, Maine’s 1st Veterinary Behaviorist – http://bit.ly/WMw-DrCalderVetBhx
Step eight – Seek help from a behavior professional. If your veterinarian determines that your dog’s behavioral issues are not the result of a medical problem, seek the advice of a professional animal behavior specialist, someone who understands canine behavior, ethology and behavior modification. Do not try to resolve this issue on your own or based on what someone tells you on Facebook. It is unlikely that you will be successful and you may make the problem worse and more difficult to resolve.
Behavior modification is not the same as dog training. Dog training is about teaching your dog to offer a particular action when given a cue. Behavior modification is about changing your dog’s emotional response to a stimulus. Aggression and reactivity are emotional responses typically based on fear or anger. Making your dog sit when a stranger approaches you and your dog is unlikely to make your dog less afraid or angry, but in fact, may make your dog feel more threatened. Behavior modification is about helping your dog develop a positive emotional response instead of barking, growling, lunging, or cowering.
The term “behaviorist” is often misused today. The only individuals that should be identifying themselves as a behaviorist are veterinarians who have been credentialed by the American College of Veterinary Behaviorists (DACVB) and applied animal behaviorists credentialed by the Animal Behavior Society (ABS). Beware of rescue and shelter workers and dog trainers that claim to be a “behaviorist” as it is unlikely that they are credentialed by the DACVB or the ABS. Below I discuss the types of qualifications that I recommend you look for when seeking behavioral help for you and your dog, and the organizations that grant those credentials.
There are three levels of professionals specializing in assisting pets with behavioral problems. You will find Professional Canine Behavior Consultants (PCBC-A) accredited by the Pet Professional Accreditation Board (PPAB) at the first level. These individuals are typically dog trainers who have completed additional education specific to behavioral disorders, passed an exam, and regularly maintain continuing education. The PPAB is currently the only accreditation body in the canine behavior and training profession that offers an independently assessed, psychometrically sound examination for Training & Behavior Consultants. In addition, it requires that those accredited follow a Code of Ethical Conduct, criteria currently lacking across other independent credentialing organizations. As a result, they are qualified to work with most behavior problems. These individuals are the ones that you will most likely find in your community.
At the next level are Certified Applied Animal Behaviorists (CAAB) and Associate Certified Applied Animal Behaviorists (ACAAB) accredited by the Animal Behavior Society (ABS). These behaviorists can work with more difficult behavior problems than the behavior consultants identified above.
At the top level are Diplomats of the American College of Veterinary Behaviorists (DACVB). These behaviorists are veterinarians with advanced training in behavior. They are skilled in dealing with the most dangerous behavior problems using both behavior modification therapy and medications.
Another place you may find help is from a veterinarian that is a member of the American Veterinary Society of Animal Behavior (AVSAB). This organization is made up of veterinarians and persons holding a Ph.D. in animal behavior or a related field. However, unlike the DACVB, ABS, IAABC, and PAAB, the AVSAB does NOT “…confer upon its members any qualifications or presuppose a level of expertise in the field of animal behavior.” The four other organizations listed above due requiring credentialed members to pass an exam and to maintain continuing education in their field. You can find links to all four of these organizations below.
Step nine – Be patient. While an undesirable behavior such as reactivity towards strangers can be created in a single event, it will likely take a significant amount of time and effort to change your dog’s behavior. Our brains and our dog’s brains work much the same. If we are exposed to something we perceive as dangerous or frightening, we are genetically pre-programmed to remember that for life. It is all about our instinctual motivation to survive. To successfully reprogram the brain can take weeks and even months of carefully planned desensitization and counterconditioning. It is human nature, especially in today’s culture to be impatient and to want instant results. That is not how behavior modification works. Be patient.
It can be very frustrating when our dog behaves anxiously or aggressively, or anywhere between these two emotional responses. Dog trainer Nancy Tanner posted an article on her blog entitled the misunderstanding of time. I encourage you to read it, and then place it somewhere you can find it quickly so that you can reread it anytime you are feeling frustrated or become impatient with your dog. < FMI – Shared Blog Post – the misunderstanding of time by Nancy Tanner – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/11/16/shared-blog-post-the-misunderstanding-of-time-by-nancy-tanner/ >
Step ten – Take care of yourself. Living with a reactive or aggressive dog is not easy and can be emotionally draining. The blog post The emotional toll of a reactive dog by Jay Gurden at Dogs Today offers some insight on taking care of yourself as you care for your dog. < FMI – Shared Article – The emotional toll of a reactive dog by Jay Gurden-Dogs Today – http://bit.ly/SharedGurenEmotional. >
I also recommend that you consider reading the book The Official Guide To Living With DINOS by Jessica Dolce. The acronym DINOS refers to Dogs In Need Of Space, which is precisely what you have when you share your life with an aggressive, reactive or fearful dog. The book is not a replacement for working with a canine behavior professional but offers constructive advice on how to live with a reactive dog. < FMI – Dogs In Need of Space – https://dogsinneedofspace.com/ >
How Can ForceFreePets Help?
I am not currently offering the seminar noted below due to COVID-19 restrictions.
ForceFreePets offers a Help! My Dog is Aggressive, Reactive, Fearful, Anxious, etc. seminar every 4 to 8 weeks. You can learn more about the next scheduled seminar at Upcoming Events page on Blog – http://bit.ly/Blog-UpcomingEvents.
For more information on Don’s behavior counseling services, 945-684, x103 or go to – http://www.greenacreskennel.com/behavior-counseling
Recommended Resources
References
2015 AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines – https://www.aaha.org/globalassets/02-guidelines/behavior-management/2015_aaha_canine_and_feline_behavior_management_guidelines_final.pdf
AVSAB Humane Dog Training Position Statement – https://avsab.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/AVSAB-Humane-Dog-Training-Position-Statement-2021.pdf
PPG Guiding Principles – https://www.petprofessionalguild.com/Guiding-Principles
Potential Causes for Reactivity (Shyness, Anxiety, Fear, and Terror) in a Dog – https://bit.ly/Causes-Reactivity
Shared Blog Post – Reactivity Misunderstood – https://bit.ly/ReactivityMisunderstood
Essential Handouts On Body Language, and Canine and Human Behavior from Dr. Sophia Yin – https://bit.ly/YinBodyLang
How Can I Tell When My Dog Is Anxious or Fearful? – http://bit.ly/DogsSignsofFear
Dog Training – Reward Based Training versus Aversives – http://bit.ly/RewardVSAversive
Shared Blog Post – Why Counterconditioning “Doesn’t Work” or How to Help Ensure Counterconditioning Will Work – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2021/11/11/shared-blog-post-why-counterconditioning-doesnt-work-or-how-to-help-ensure-counterconditioning-will-work/
Shared Blog Post – the misunderstanding of time by Nancy Tanner – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/11/16/shared-blog-post-the-misunderstanding-of-time-by-nancy-tanner/
What Is A Pet Behavior Consultant? – http://bit.ly/WhatIsPetBhxConsulting
Introduction to Canine Communication – http://bit.ly/CanineComm
Dominance: Reality or Myth – http://bit.ly/Dominance-RealityorMyth
Understanding, Identifying and Coping with Canine Stress – http://bit.ly/Canine-Stress
Canine Behavior – Myths and Facts – Part 1, Where do we get our knowledge about dogs? – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/05/04/canine-behavior-myths-and-facts-part-1-where-do-we-get-our-knowledge-about-dogs/
Green Acres Kennel Shop Position Statement on the Use of Dominance and Punishment for the Training and Behavior Modification of Dogs – http://bit.ly/GAKS-Pos-NoPain-NoForceNoFear
The Unintended Consequences of Shock Collars – http://bit.ly/ShockCollars
The emotional toll of a reactive dog by Jay Gurden in Dog’s Today – http://bit.ly/SharedGurenEmotional
Important Position Statements Related to Animal Welfare & Care in the USA by Leading Organizations – https://bit.ly/Pos_HumaneTraining
What’s Shocking about Shock? – What Science Tells Us About the Use of Shock in Dog Training – PPG BARKS from the Guild – July 2019 – http://bit.ly/ShockBARK-JUL2019
Things I Wish I Had Known Before I Started Training Dogs – Gus, the Dominance Myth, An Alpha Roll, and a Damaged Relationship – WWM-SEP2018 – http://bit.ly/Things-Gus-Dominance
Things I Wish I Had Known Before I Selected My First Dog – Aversives are Unnecessary and Counter-Productive When Training A Dog – Part 1 – WWM-JAN2019 – http://bit.ly/Things-Aversives-1
Things I Wish I Had Known Before I Selected My First Dog – Aversives are Unnecessary and Counter-Productive When Training A Dog – Part 2 – WWM-FEB2019 – http://bit.ly/Things-Aversives-2
Choke Collar Pathology – an excellent blog post from dog trainer Daniel Antolec on the dangers of using a choke collar on a dog. – http://ppgworldservices.com/2017/06/13/choke-collar-pathology/

Canine Behavior: Myths & Facts – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/03/27/podcast-canine-behavior-myths-and-facts/
Pet Behavior, Vets & The AAHA Canine and Feline Behavior Management Guidelines with Dr. Dave Cloutier from Veazie Veterinary Clinic – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2016/03/13/podcast-the-woof-meow-show-pet-behavior-vets-the-aaha-canine-and-feline-behavior-management-guidelines-with-dr-dave-cloutier-from-veazie-veterinary-clinic/
Dog Training Questions for Don and Kate with special guest host Dr. Mark Hanks – part 3 – http://blog.greenacreskennel.com/2015/07/27/blog-post-27jul15-podcast-dog-training-questions-for-don-and-kate-with-special-guest-host-dr-mark-hanks-part-3/
The Unintended Consequences of Shock Collars – http://bit.ly/ShockPodcast
The Pet Professional Guild and the Shock-Free Coalition with Niki Tudge – http://bit.ly/PodCastShockFree-NikiTudge-2017
What’s Shocking About Shock – What Science Tells Us About the Use of Shock in Dog Training – http://bit.ly/WfMw-WhatShock-27JUL19
Podcast – Charlee and the Electronic Shock Containment System w-Dan Antolec – https://bit.ly/Blog-Charlee_E-Fence
To Find A Qualified and Credential Animal Behavioral Specialist
American College of Veterinary Behaviorists (ACVB) – https://www.dacvb.org/search/custom.asp
Animal Behavior Society ( ABS ) Certified Applied Animal Behavior Consultants – http://www.animalbehaviorsociety.org/web/applied-behavior-caab-directory.php
Pet Professional Accreditation Board (PPAB) – https://www.credentialingboard.com/Professionals
________________________________________________________________________
Don Hanson lives in Bangor, Maine, where he is the co-owner of the Green Acres  Kennel Shop ( greenacreskennel.com ) and the founder of ForceFreePets.com, an online educational resource for people with dogs and cats. He is a Professional Canine Behavior Consultant (PCBC-A) accredited by the Pet Professional Accreditation Board (PPAB) and a Bach Foundation Registered Animal Practitioner (BFRAP). Don is a member of the Pet Professional Guild (PPG), where he serves on the Board of Directors and Steering Committee and chairs the Advocacy Committee. He is also a founding director of Pet Advocacy International (PIAI). In addition, Don produces and co-hosts The Woof Meow Show podcast, available at http://bit.ly/WfMwPodcasts/, the Apple Podcast app, and Don’s blog: www.words-woofs-meows.com. The opinions in this post are those of Don Hanson.
Kennel Shop ( greenacreskennel.com ) and the founder of ForceFreePets.com, an online educational resource for people with dogs and cats. He is a Professional Canine Behavior Consultant (PCBC-A) accredited by the Pet Professional Accreditation Board (PPAB) and a Bach Foundation Registered Animal Practitioner (BFRAP). Don is a member of the Pet Professional Guild (PPG), where he serves on the Board of Directors and Steering Committee and chairs the Advocacy Committee. He is also a founding director of Pet Advocacy International (PIAI). In addition, Don produces and co-hosts The Woof Meow Show podcast, available at http://bit.ly/WfMwPodcasts/, the Apple Podcast app, and Don’s blog: www.words-woofs-meows.com. The opinions in this post are those of Don Hanson.
©22MAY22, Donald J. Hanson, All Rights Reserved
< Click for Copyright and Use Policy >
 In a November 2014 blog post from the dodo, Marc Bekoff, professor emeritus of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and a Fellow of the Animal Behavior Society, discusses this episode, Showdown with Holly, and a slow-motion version of the show entitled Show Down with Holly in Slow Motion – A dissection of canine body language. The latter adds commentary that points out the body language used by Holly to indicate that she was feeling threatened. It also illustrates the additional
In a November 2014 blog post from the dodo, Marc Bekoff, professor emeritus of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and a Fellow of the Animal Behavior Society, discusses this episode, Showdown with Holly, and a slow-motion version of the show entitled Show Down with Holly in Slow Motion – A dissection of canine body language. The latter adds commentary that points out the body language used by Holly to indicate that she was feeling threatened. It also illustrates the additional  visual signals Holly uses in an attempt to de-escalate the confrontation. Milan was either unaware of these signals and their importance (I didn’t see that coming!) or simply chose to ignore them. Milan is bitten when he moves the same hand he used to punch Holly near her face. < click to view > NOTE: You will need to click on “Uncover Video.”
visual signals Holly uses in an attempt to de-escalate the confrontation. Milan was either unaware of these signals and their importance (I didn’t see that coming!) or simply chose to ignore them. Milan is bitten when he moves the same hand he used to punch Holly near her face. < click to view > NOTE: You will need to click on “Uncover Video.”